Oh no, migraine is attacking soon!
The current medications used and other natural approaches for migraine
22 Oct 2024 | Chin

Introduction and Current Trends
Migraine is a debilitating neurological condition that affects about 17% of women and 6% of men worldwide. As one of the disability diseases, migraine comes with symptoms ranging from moderate to severe headaches, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound, managing migraines can be challenging. Recent trends in migraine management are focused on a personalized approach, which includes medication, lifestyle modifications, and even natural remedies. A Novartis Migraine Survey (2020) reported that 27% of Malaysians avoid triggers, while most resort to painkillers for relief.
Pathophysiology of Migraine
Migraines are believed to stem from complex interactions between the brainstem, nerves, and blood vessels. These interactions lead to inflammation and dilation of blood vessels in the brain, triggering pain signals. Additionally, imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) are linked to migraine attacks.
How People Normally Deal with Migraines
Avoiding Triggers
Common triggers include certain foods, strong odors, bright lights, and stress. Many migraine sufferers try to minimize exposure to known triggers, such as avoiding processed foods or reducing stress through mindfulness techniques.
Taking Medication
Painkillers like ibuprofen or triptans are frequently used to manage migraine pain. However, pharmaceutical treatments may cause side effects such as nausea or exhaustion. Many people take medications as a first line of defense to control symptoms.
Resting or Sleeping
A nap or resting in a quiet, dark room is another common strategy. Photophobia may trigger migraine as well. Migraines often come with fatigue, and resting can help reduce the severity or duration of an attack. For some, sleep may be the only way to alleviate symptoms.
Current Medical Approaches for Migraine Relief
- Pharmaceutical Treatments
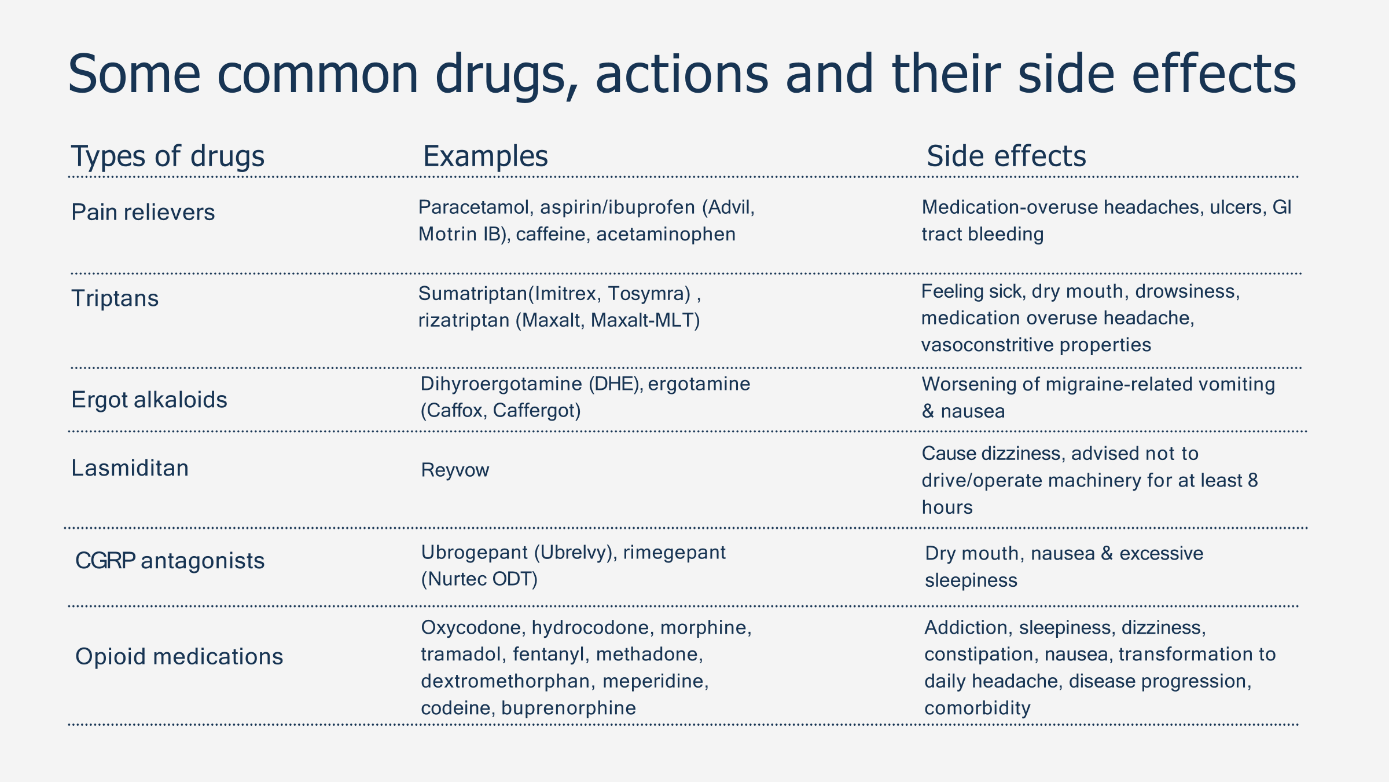
Medications like triptans, ergot alkaloids and CGRP inhibitors are commonly prescribed, but they come with potential side effects such as nausea and gastrointestinal issues. While effective for some, their limited effectiveness for others underscores the need for alternative therapies.
2. Natural Remedies
Herbs such as feverfew, ginger, and peppermint oil are gaining popularity due to their ability to target migraine-related inflammation and pain. For instance, peppermint oil’s menthol has soothing effects, while feverfew has been studied for its anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Botox Injections
Botox has been approved for chronic migraines. Administered every few months, these injections help prevent migraine episodes by blocking pain signals. Though effective for some, Botox is typically reserved for those with frequent, debilitating migraines.
4. Lifestyle and Behavioral Therapies
Stress management through yoga, meditation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines. These approaches address the emotional and psychological triggers that often exacerbate migraines.
5. Dietary Supplements
Magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and Coenzyme Q10 are among the supplements shown to help prevent migraines. These supplements work by supporting brain health and reducing inflammation, offering a more natural route for long-term migraine management.
What we have in Goodness Through Food for Migraine?

MiBRAiNE
Formulated with botanical formula feverfew and magnesium which work synergistically to prevent inflammation and induced vasospasm in the brain.
How does the ingredients help?
Parthenolide and Tanetin are compounds that help reduce inflammation by blocking certain pathways. Parthenolide inhibits a key enzyme involved in inflammatory signaling and the production of inflammatory prostaglandins. Tanetin prevents the release of inflammatory substances like arachidonic acid, inhibits blood platelet clumping, and blocks immune cell activities related to inflammation. Magnesium helps with relaxation and calming of the nervous system.
GTF Worldwide Sdn Bhd
- No. 20-2, Plaza Danau 2, Jalan 5/109F, Taman Danau Desa, 58100 Taman Desa, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
- (03) 7982 9881
- (012) 483 5523
- info@gtf.com.my
